Table of Contents
1. Diabetes in Singapore
Diabetes is a life-changing diagnosis that mandates numerous lifestyle modifications and the intake of drugs to keep your blood sugar - also called blood glucose - under control.
The incidence of this disease has been rising over the past few decades, which may be the result of our new lifestyle, obesity, and sedentary lifestyles. In Singapore, there were 440,000 cases of diabetes in 2014. Experts believe this number will reach one million cases in 2050. Relative to other countries, Singapore has an unusually high incidence and prevalence of diabetes. This chronic condition has such dangerous complications and involves such long-term cost burden on individuals and the healthcare system that the Singapore government declared the ‘War on Diabetes’ in 2016.
In this article, we will discuss the different aspects of diabetes, including diabetes symptoms, complications, risk factors, treatments and self-management for this chronic disease.
2. What is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a chronic condition characterised by persistently elevated blood glucose levels (also called blood sugar levels). The high glucose levels in the blood vessels wreak havoc on most organ systems. There are three types of diabetes:
- Type 1 diabetes – also known as insulin-dependent diabetes
- Type 2 diabetes – the most common type of diabetes
- Gestational diabetes – occurs during pregnancy
In type 1 diabetes (T1D), the body fails to make enough insulin, often due to genetic causes, while in type 2 diabetes (T2D), the body’s insulin production and processing function worsens over time, often due to lifestyle causes or age. By far, T2D is the most prevalent in Singapore and worldwide. Many T2D cases start out as prediabetes - a period where blood glucose level is higher than normal but not high enough to be diagnosed as diabetes.
You might be wondering, “what is exactly the function of insulin?”
In simple terms, insulin is a hormone made in the pancreas and is responsible for activating the receptor that allows glucose molecules to enter the cell. If the action of insulin is not effective at stimulating this receptor, glucose cannot enter the cell. Glucose is needed in the body for energy. Without glucose, the body is functioning like a machine without gasoline.
For decades, researchers believe that insulin resistance is the exclusive dysfunction in Type 2 diabetes. However, recent evidence indicates that insulin production becomes suboptimal over the years due to the slow destruction of the pancreatic tissue. In the beginning, the pancreas is relatively intact with the normal production of insulin. However, because the cells do not respond well to the action of this hormone, more and more insulin is needed by the body over time, leading to an overworked and gradually weakened pancreas. The combination of insulin resistance and its relative deficiency are the hallmarks of diabetes pathology.
Type 2 diabetes is common in obese individuals above the age of 40. These patients tend to have several risk factors of diabetes (more on that later). Type 1 diabetes however is often diagnosed before the age of 40, commonly among children under 14 years old. In recent years, we are seeing a surge in cases of Type 2 diabetes in young individuals. Experts attribute this phenomenon to the obesity epidemic.
3. What Causes Type 2 Diabetes?
The exact causes of T2D are not fully understood due to the complexity of this disease. Nevertheless, researchers settled on the concept of ‘nature and nurture’ to explain this illness. Let us quickly decipher this concept:
The ‘nature’ cause of Type 2 diabetes
Having a family history of T2D increases your risk of developing this condition relative to the general population. In one study, researchers found that having a family history of T2D increases your risk by 2.5-fold. Add obesity to the equation, and your risk shoots up to 20-fold.
The ‘nurture’ cause of Type 2 diabetes
While genetics may play a role in T2D, lifestyle habits seem to be the primary drivers of this condition. Obesity is by far the most important risk factor, especially when the fat tissue is located around the abdominal and waist region. Scientists noted that consuming a carbohydrate-rich diet for a long time leads to a vicious cycle of glucose and insulin spikes. As a result, the cells become less sensitive to the action of insulin.
Another important aspect of the nurture part is consuming foods with high glycemic indexes. This concept refers to how fast your blood sugar rises after eating a certain food. The faster your blood glucose rises, the higher the glycemic index. For instance, soda and synthetic juices primarily contain simple sugars, which translates into a high glycemic index.
Risk factors of T2D include:
- Overweight or obesity: individuals with BMI of 25 and above according to WHO
- Genetics: having a first degree relative or family member diagnosed with diabetes
- Age: over 95% of diabetes cases in Singapore are diagnosed among those aged 40 and above
- Race: diabetes incidents among Indians and Malays are twice as high as Chinese among Singaporeans aged 60 and above)
- Women with polycystic ovarian syndrome
The early diagnosis of diabetes is crucial to prevent complications and improve prognosis. For this reason, Singaporeans with risk factors of diabetes are advised to get regular screenings to prevent and detect T2D. With the Screen for Life programme, you can get subsidised or free diabetes screening for just $5 or lower, instead of the average usual cost of $100.
4. Diabetes Symptoms
Diabetes presents with a variety of signs and symptoms that overlap with all types. For this reason, it is challenging to differentiate between the different types of diabetes without additional information such as the patient's age and general health profile, pregnancy status, family history. A blood test may reveal hyperglycemia - the medical term for high blood sugar, but hyperglycemia can be non-diabetic. Therefore, it is best to consult a specialist for your specific condition.
Here are some of the signs and symptoms of Type 2 diabetes:
- Feeling hungry and eating multiple times a day
- Excessive thirst and drinking a lot of water
- Excessive urination
- Dry mouth
- Fatigue
- Itchy skin
- Unexplained weight loss
5. Complications of Type 2 Diabetes
Persistently high glucose levels in the blood can damage other parts of the body. Diabetes is challenging because it is an ‘invisible disease’ in the early stage. In some cases, the condition is detected when it has progressed and caused complications on other parts of the body, such as a stroke, decreased vision loss, glaucoma, a heart or cardiovascular disease, or an infection that keeps unhealed.
Common complications of Type 2 diabetes include:
- Kidney damage (diabetic kidney disease): diabetes can cause the kidney to malfunction over time, leading to kidney failure in serious cases. In fact, diabetes is the top cause of kidney failures in Singapore. Individuals with diabetes are recommended to regularly screen for kidney diseases from the point of diabetes diagnosis, to prevent kidney damage from happening or deteriorating into kidney failure. Read more about the linkage between diabetes and kidney diseases and how to prevent kidney failures among diabetics in our article here.
- Nerve damage (diabetic neuropathy): the nerves are damaged as a result of diabetes, in various parts of the body such as in the legs, feet, heart or blood vessels. Depending on the body parts where nerves are affected, diabetic neuropathy conditions may manifest into different health conditions.
- Hearing impairment: when the nerves in the ear are damaged, hearing is affected. This type of hearing loss is non-irreversible.
- Diabetic ulcer: nerve damage can also cause poor circulation, leading to ulcers. Serious or untreated ulcers may lead to amputation.
- Diabetic retinopathy: when the blood vessels in the retina are affected, the person may experience vision loss and even blindness.
- Diabetic ‘stomach’ or diabetic gastroparesis: when the nerves in digestive tracts are damaged, diabetes patients may experience digestive issues such as constipation, heartburn or nausea.
- Glaucoma: The chances of developing glaucoma is believed to double for diabetic patients.
- Infections: Diabetes lowers the body’s immunity. Diabetic patients therefore are more prone to infections. They also have more difficulty healing infections and wounds.
- Increased risk of heart and cardiovascular diseases: People with diabetes are at 2 to 4 times higher risk of cardiovascular disease compared to those without, including stroke and coronary artery disease. Read more about the risk of heart and cardiovascular diseases in elderlies here.
- Increased risk of Alzheimer’s disease: Research has found such a strong connection between the two conditions that Alzheimer’s is sometimes unofficially referred to as Diabetes Type 3. Long-term presence of high levels of glucose in blood streams is believed to cause cognitive impairment.
Diabetes type 2 may cause an acute complication known as hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (HSS). When this happens, blood sugar shoots up to an extremely high level, causing water loss and other life-threatening consequences, and thus requires immediate medical care.
6. Diabetes Treatment
Before starting you on diabetes medications, your doctor will recommend a few lifestyle modifications that focus on eating a healthier diet and becoming more active.
After a trial of 3 months, your doctor will reorder some tests to see the efficacy of the diet and exercise. If your blood sugar drops to normal levels and your symptoms disappear, you may not need any pharmacological drugs.
Otherwise, you can expect the following treatments:
- Metformin
Metformin is the drug of choice to treat Type 2 diabetes. It lowers the production of glucose in the liver and increases the storage of glycogen inside the muscles. Additionally, metformin promotes weight loss, which further helps patients to control their glucose levels.
- Sulfonylureas
These drugs work by stimulating the pancreas to produce more insulin. However, there is a risk of hypoglycemia (i.e., low blood sugar), especially if you take a higher dosage than recommended.
- Other oral drugs
- Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors
- Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists
- Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors
- Meglitinides
- Thiazolidinediones
- Insulin
When oral hypoglycemic drugs do not improve your symptoms, your doctor may opt for insulin therapy to restore the balance in your body. Unfortunately, many patients fail to comply with insulin therapy due to the high frequency of injections. The result of chronically elevated blood sugar and poor compliance with treatments is one or more of the complications we cited above.
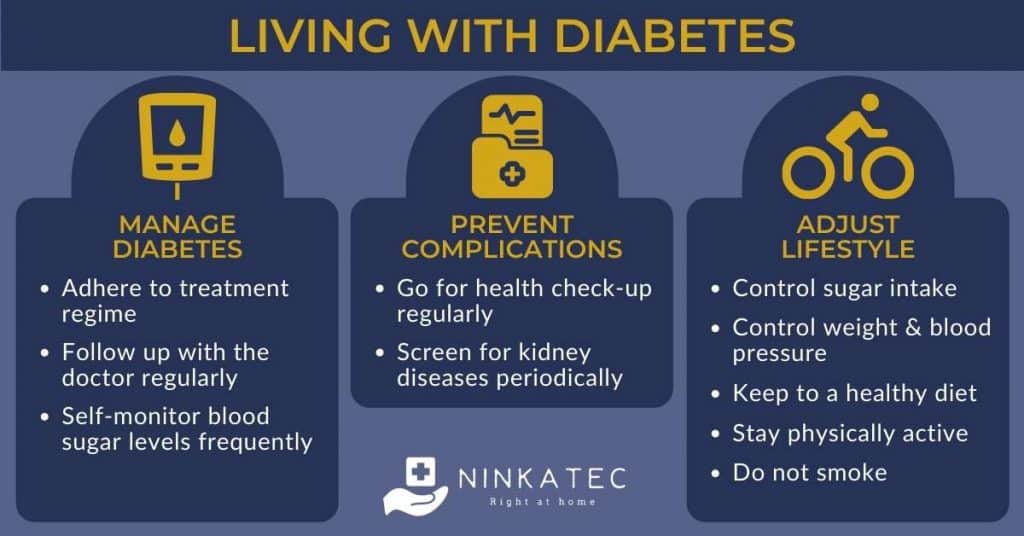
7. Living with Diabetes
Like all chronic illnesses, there is no complete cure. Treatment of diabetes involves lifelong measures to control the condition, much of which is self-administered by the patient at home by adjusting or limiting lifestyle factors that exacerbate the development of the condition, such as weight management, quitting smoking, and engaging in regular physical exercise activities.
Diet is indispensable to restore blood sugar balance and prevent complications. Here are a few diet recommendations that may help with diabetes:
Whole foods, fruits, and vegetables
In a 2016 study, 32 diabetic participants followed the paleo diet for 3 months. At the end of the study, all participants lost weight and had better blood sugar levels, improved insulin sensitivity, and more secretion of ghrelin which is a hunger-suppressing hormone.
Unsaturated fatty acid-rich
Fish oil is very healthy for the body. It dampens inflammation, neutralizes oxidative stress, and regulates blood sugar levels.
Omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids also promote weight loss. In a 2010 study, researchers supplemented 46 participants with daily fish oil for 6 weeks. The results of the study showed that participants lost an average of 0.5 kilograms and had improved glycemic control. Moreover, blood cortisol concentration dropped, which is a hormone that can increase glucose levels.
Green leafy vegetables
Several studies demonstrated the positive effects of consuming leafy vegetables on diabetes. Foods such as kale, broccoli, and spinach are rich in fiber and antioxidants – both compounds improve blood sugar levels. In one study, researchers concluded that consuming 1.5 servings of green leafy vegetables per day lowers your risk of T2D by 14%.
8. Managing Diabetes at Home with Ninkatec
Ninkatec is one of the leading home care service providers in Singapore. We use advanced medical technology to help patients live more meaningfully right at home. In the War on Diabetes, we stand with the nation to help diabetes patients monitor their conditions and manage complications better at home. Through the use of medical technology, we help to monitor patient’s vital signs and provide instant online chat support in case patients or family members have enquiries. Our doctors and nurses also visit patients at their homes when necessary, saving patients and families the hassle of travelling to clinics and hospitals. Check out our Chronic Disease Management service for more details, or chat with our Care Team about your conditions for a private consultation.